In the cozy corners of our homes, where purring cats and tail-wagging dogs fill our hearts with boundless joy, lies a silent guardian of their health and happiness—vaccination. Just as a knight’s armor protects him from unseen perils, vaccines shield our beloved pets from a host of lurking diseases. Imagine a world where your furry companions can frolic freely, chasing butterflies and basking in the sun, all because they’ve been armed with the best defense modern veterinary medicine can offer. In this heartwarming journey, we’ll explore the pivotal role that vaccination plays in ensuring our pets lead long, vibrant lives, and how a simple prick can make all the difference in their well-being. So, grab a cup of tea, cuddle up with your pet, and let’s delve into the fascinating world of pet vaccinations together.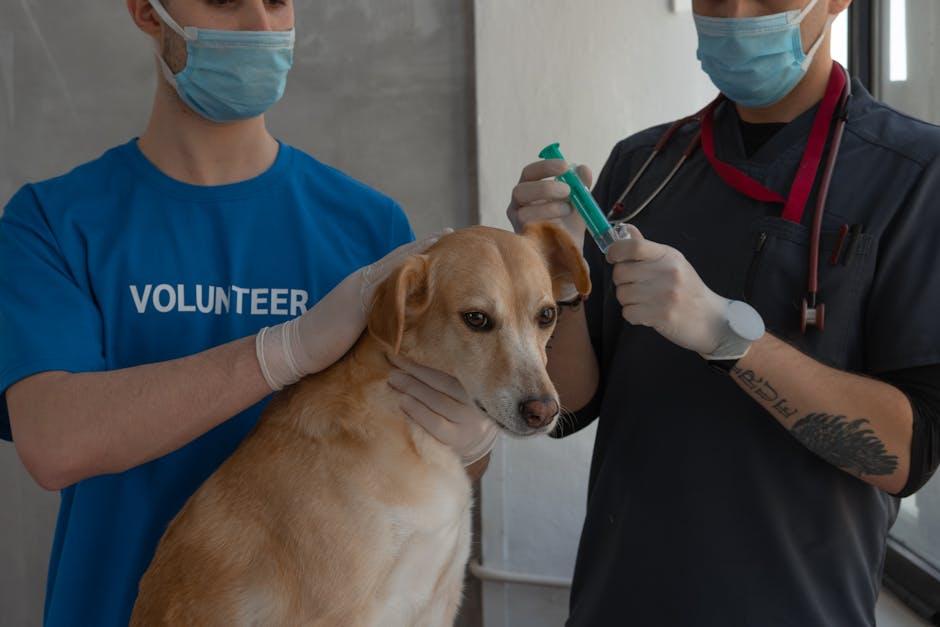
Shielding Our Furry Friends: The Science Behind Pet Vaccinations
Vaccinations are more than just a routine part of your pet’s healthcare; they are a crucial defense mechanism that shields them from a myriad of diseases. The science behind pet vaccinations involves introducing a harmless component of the disease-causing organism into your pet’s body. This stimulates their immune system to recognize and fight off the actual pathogen if they ever encounter it in the future. By doing so, vaccines not only protect individual pets but also contribute to the broader concept of herd immunity, making the environment safer for all animals.
Here are some of the key benefits of vaccinating your pets:
- Prevention of serious diseases: Vaccines protect against illnesses such as rabies, parvovirus, and distemper, which can be fatal.
- Cost-effective: Treating diseases can be expensive and emotionally taxing. Vaccinations are a preventive measure that saves both money and heartache.
- Community health: Vaccinated pets help to prevent the spread of contagious diseases, safeguarding other animals and even humans.
- Legal requirements: In many areas, certain vaccinations are mandated by law, such as rabies shots for dogs and cats.
By understanding and embracing the science behind pet vaccinations, you are making a proactive choice to ensure the well-being of your furry friends and the community they live in.
Common Pet Diseases and How Vaccines Combat Them
Vaccinations play a pivotal role in safeguarding our beloved pets from a myriad of diseases that could otherwise compromise their health and well-being. Among the most common ailments, canine parvovirus, distemper, and rabies stand out as particularly menacing for dogs. For our feline friends, feline leukemia virus (FeLV), feline immunodeficiency virus (FIV), and panleukopenia pose significant threats. Vaccines work by stimulating the immune system to recognize and combat these pathogens effectively, providing a shield of protection that can prevent outbreaks and severe health complications.
Here are some of the prevalent diseases and the vaccines that help combat them:
- Canine Parvovirus: A highly contagious viral illness that affects dogs, particularly puppies. The parvovirus vaccine is essential in preventing this deadly disease.
- Distemper: Another severe viral infection in dogs, distemper can affect the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems. Vaccination is crucial to protect against this multifaceted virus.
- Rabies: Known for its ability to affect both pets and humans, rabies is a fatal disease. Regular rabies vaccinations are not only important for your pet’s health but are often required by law.
- Feline Leukemia Virus (FeLV): This virus can cause cancer and immunosuppressive conditions in cats. Vaccinating your cat can prevent FeLV transmission and its associated health issues.
- Feline Immunodeficiency Virus (FIV): Often compared to HIV in humans, FIV weakens a cat’s immune system. Vaccines can help reduce the risk of infection and support overall health.
- Panleukopenia: Also known as feline distemper, this disease is highly contagious and often fatal. The panleukopenia vaccine is a core component of feline vaccination protocols.
By staying diligent with vaccination schedules, pet owners can significantly reduce the risk of these common diseases, ensuring a healthier, happier life for their furry companions.
Crafting a Vaccination Schedule: Timing and Types for Maximum Protection
Establishing a well-planned vaccination schedule is essential for safeguarding your pet’s health. Timing is crucial, as it ensures that vaccines are administered when your pet’s immune system is most responsive. Typically, the initial vaccines are given to puppies and kittens at 6-8 weeks of age, followed by booster shots every 3-4 weeks until they are around 16 weeks old. Adult pets also require regular booster shots to maintain immunity.
Different vaccines protect against various diseases, and understanding which ones your pet needs is vital. Here are some common vaccines:
- Core vaccines: These are essential for all pets and include rabies, distemper, parvovirus, and adenovirus.
- Non-core vaccines: These are recommended based on your pet’s lifestyle and risk factors. They include Bordetella, Lyme disease, and leptospirosis.
Consulting with your veterinarian will help tailor a vaccination schedule that provides maximum protection for your furry friend.

Beyond the Basics: Boosters and Additional Vaccinations for Special Cases
While core vaccinations are crucial for all pets, certain animals may require boosters and additional vaccines tailored to their unique circumstances. These special cases often include pets with compromised immune systems, those living in high-risk environments, or animals traveling internationally. Tailoring a vaccination plan ensures that your furry friend receives the optimal level of protection against potential health threats.
Consider the following scenarios where extra vaccinations might be necessary:
- Senior pets: As animals age, their immune systems may weaken, making them more susceptible to diseases. Regular boosters can help maintain their immunity.
- Pets with chronic illnesses: Pets suffering from conditions like diabetes or kidney disease may benefit from additional vaccinations to prevent complications.
- Pets in multi-animal households: If you have multiple pets, one infected animal can quickly spread disease to others. Extra vaccinations can help prevent outbreaks.
- Pets traveling abroad: Different countries have varying disease risks and vaccination requirements. Ensure your pet is protected and compliant with local regulations.
Consulting with your veterinarian about these special cases will help you devise a comprehensive vaccination strategy, ensuring your pet’s long-term health and happiness.


































